Abstract
Introduction
Myelofibrosis (MF) is characterized by cytopenias, splenomegaly, burdensome symptoms, and poor overall survival (OS). To date, few studies have investigated if earlier intervention with targeted MF therapies affects response and OS. In a pooled analysis of the COMFORT I and II trials of ruxolitinib (RUX), the first approved treatment for MF, patients (pts) who received RUX at randomization or after crossover from placebo (PBO) or best available therapy (BAT) had improved OS. The survival advantage in the crossover group was less than that among pts initially randomized to RUX, suggesting that earlier intervention may provide greater clinical benefit. Additionally, previous reports have shown that pts earlier in their disease course (lower- vs higher-risk category or grade of bone marrow fibrosis) and those who initiated RUX earlier (≤2 y vs >2 y from diagnosis) had improved responses to RUX. The objective of this analysis was to assess the association of MF disease duration before treatment with disease outcomes using pooled COMFORT data.
Methods
COMFORT I (NCT00952289) and COMFORT II (NCT00934544) were phase 3 trials of RUX vs PBO or BAT, respectively, in pts with intermediate-2 or high-risk MF. In this post hoc analysis, data from RUX-treated pts in both studies were combined (RUX treatment group), and data from the PBO/BAT arms were pooled (control group). Pt subgroups were defined based on disease duration before RUX initiation (≤12 mo or >12 mo from diagnosis). Assessments included frequency of thrombocytopenia (platelets [PLT] <100 Gi/L or PLT transfusion) and anemia (hemoglobin <100 g/L or red blood cell transfusion) events, spleen volume response (SVR; spleen volume reduction ≥35% from baseline [SVR35]), symptom response (MF-Symptom Assessment Form total symptom score [TSS] reduction ≥50% from baseline [TSS50]; available in COMFORT I only), and OS. OS was assessed using the Kaplan-Meier method; pts randomized to PBO/BAT were included in the PBO/BAT group regardless of crossover.
Results
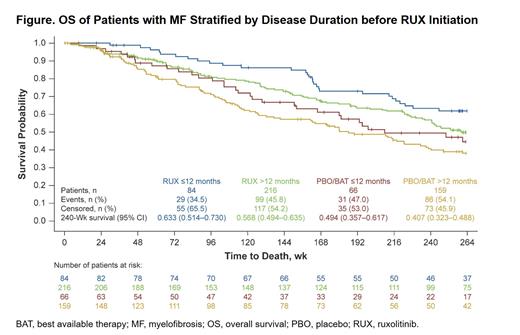
A total of 525 pts were included in the analysis (RUX: ≤12 mo, n=84; >12 mo, n=216; PBO/BAT: ≤12 mo, n=66; >12 mo, n=159). Median age across groups ranged from 65.0 to 70.0 y. Baseline clinical characteristics were generally similar across subgroups, although pts with shorter vs longer disease duration were slightly younger and tended to have higher blood counts. Among pts who received RUX, fewer thrombocytopenia events were observed among those who initiated treatment earlier (≤12 mo vs >12 mo), with differences observed as early as Wk 4-8 on treatment (18% vs 33%) and sustained over time; a similar trend was observed for anemia events (Wk 4-8, 59% vs 72%). Mean (SD) reduction from baseline in spleen volume was greater for pts who initiated RUX at ≤12 mo vs >12 mo at Wk 24 (-35% [21] vs -29% [18]) and Wk 48 (-36% [24] vs -28% [22]). Likewise, the proportion of pts with SVR35 was greater among those who initiated RUX earlier (≤12 mo vs >12 mo) at Wk 24 (48% vs 33%) and 48 (44% vs 27%). Spleen responses were more durable among those with shorter vs longer disease course (median duration of response, not reached vs 230 wk, respectively). A greater proportion of pts who initiated RUX at ≤12 mo vs >12 mo achieved TSS50 at Wk 24 (56% vs 40%); mean (SD) change from baseline in TSS at Wk 24 was -52% (42) vs -44% (51), respectively. OS at Wk 240 was improved among pts who initiated RUX at ≤12 mo vs >12 mo (63% [95% CI, 51%-73%] vs 57% [95% CI, 49%-64%]; P=0.0430; Figure). Comparatively, OS was longer with RUX vs PBO/BAT regardless of disease duration. A sensitivity analysis using a 24-mo cutoff was also conducted but yielded weaker associations between disease duration and SVR, TSS, and OS.
Discussion
These findings suggest that earlier RUX initiation in MF may improve clinical outcomes, including fewer cytopenia events, durable spleen volume response, symptom burden, and OS. Although younger age and higher baseline blood counts may have been confounders for improved clinical outcomes in this study, these factors likely reflect an earlier disease stage, and the observed outcomes support the rationale for early intervention in a real-world setting. While "watch and wait" remains a common treatment approach for newly diagnosed patients, these data suggest that patients with MF may benefit from earlier intervention. Additional studies to further evaluate the impact of early intervention are warranted.
Verstovsek: Incyte Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; CTI BioPharma: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Ital Pharma: Research Funding; Protagonist Therapeutics: Research Funding; PharmaEssentia: Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines Corp: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sierra Oncology: Consultancy, Research Funding; Constellation: Consultancy; Pragmatist: Consultancy. Kiladjian: Taiho Oncology, Inc.: Research Funding; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; PharmaEssentia: Other: Personal fees; Incyte Corporation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AOP Orphan: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Vannucchi: Incyte Corporation: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Mesa: Genentech: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; La Jolla Pharma: Consultancy; AOP: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Samus: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; CTI: Research Funding; CTI: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Pharma: Consultancy; Constellation Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Research Funding; Incyte Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sierra Oncology: Consultancy, Research Funding. Scherber: Incyte Corporation: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company. Hamer-Maansson: Incyte Corporation: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Harrison: Incyte Corporation: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Promedior: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Shire: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; AOP Orphan Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Sierra Oncology: Honoraria; Constellation Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Galacteo: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Keros: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Gilead Sciences: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Geron: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; CTI BioPharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal